To live in Australia, we not only have to follow the customs and abide by Australian laws, but also pay taxes according to the Australian tax system and return taxes. Of course, we can also get the tax rebate due.
No matter where you come from, whether you know English or not, tax returns are required. Therefore, it is very necessary to understand the relevant common sense of Australian tax returns.
A brief introduction to Australia's tax system

Australia is a federal country, after a long period of evolution and development, a sound and scientific tax system has been established in Australia.
Australia's tax system has formed its own characteristics in many aspects. It has not only a reasonable tax system, but also a unique tax management system and a rigorous and effective tax audit mechanism. Thus, the smooth implementation of the tax system is guaranteed. Australia is a high welfare, but also a high tax country. The personal income tax burden is significantly higher than in China, and taxpayers are required to pay a welfare insurance tax at 1.5% of their taxable income tax.
Practical knowledge of tax rebate in Australia
1. Application for tax numbe
In Australia, whether it is work or study abroad, you should apply to the individual's tax number as soon as possible (Tax File Number). To remind you, the individual's tax number is the confidential information, do not disclose to others at will! Only the bank and other agencies can ask you to provide the tax.
Read: handle to teach you to apply for Australian tax number (TFN)
2. What is "Fiscal year Financial Year"?
The Chinese who have just come to Australia may be odd: it is called Financial Year on July 1, the year of the year. One Year is not from January 1 to December 31! The period from July 1 to June 30, from July 1, to June 30, is also the calculation cycle of the individual's annual income.
So, how much income you have in Australia, how much tax should be called, not in accordance with the natural year, but in accordance with the fiscal year said here.
3. Annual tax filing time
The period from July 1 to October 31 of each year is the statutory tax return period. If you entrust an accountant to return, it can be extended to March 31 of the following year. You must declare a personal income tax for the previous fiscal year to the ATO during this period.
4. Major taxes
Australia is a tax-sharing country, its tax revenue is divided into central tax revenue and local tax revenue. Federal taxes include: personal income tax, corporate income tax, sales tax, welfare insurance tax, tariff, consumption tax and other taxes, as well as federal state-owned enterprises to pay profits and so on.
State goverment taxes include: payroll tax, stamp duty, financial institution tax, land tax, debt tax and other taxes.
Australia is different from other tax-sharing countries in that it has different main taxes: Australia's main taxes are direct taxes, and the personal income tax in direct taxes is the top priority.
Individual income tax is about 60% of the total federal tax revenue. Other main taxes, such as China, are indirect taxes.
5. Personal request for filing tax returns
Australia's tax code requires any Australian tax resident, whether his income comes from within or outside Australia, to file his income tax with the Australian Revenue Authority, (ATO). Generally speaking, individuals whose residence is within Australia or stay in Australia for more than 183 days are likely to be considered as Australian tax residents and subject to tax obligations as long as they reside in Australia or stay in Australia for more than 183 days.
An individual who does not have permanent residence or citizenship does not represent an exemption from tax obligations as the Australian Inland Revenue Authority assesses whether an individual is a tax resident, in addition to taking into account the factors of domicile and number of days of residence. Other factors, such as the location of one's main business, whether or not he intends to live in Australia for a long time, will also be taken into account, and international students are tax residents.
Caution: when applying for a tax number, many foreign student friends have an option to ask if you are "Resident on Tax Purpose" and do not mistakenly think that you are an Australian resident or an PR, but whether you are an Australian tax resident, and if this condition is met, It should be chosen.
6. Preparation of tax filing materials
There are a variety of documents for tax returns, including:
- Tax return group certificate or last year's tax record tax return orassessment notice;
- Payroll;
- All other income records, such as pensions, benefits, sale of shares, income from rent;
- All expenditure vouchers related to work, business, and financial investment (receipts, invoices, airline tickets, bills, private health care numbers, income and expenditure documents for spouses and children, valid notes, etc.);
- The account book of the company or the small business;
- If you have some expenses without vouchers, such as train tickets, as long as there is a reasonable calculation method, the Inland Revenue Department is also approved.
All tax returns will be kept for five years, as the Inland Revenue Department will conduct random checks every year.
In random checks, everything is based on evidence, but occasionally a reasonable "forget" can also be accepted by the tax officer. If a false overstatement is verified, there will be a lot of fines, at least 13% of the annual income.
Generally speaking, work-related expenses, less than $300, generally do not require vouchers, can be recorded on their own to obtain a tax rebate.
7. e-tax Submission
One of the easiest ways to file online tax returns is to use the online e-tax (electronic tax filing software). E-tax is a free-of-charge electronic tax filing system on the Australian Inland Revenue Authority's website, available 24 hours a day.
As long as you search for E tax on the ATO website, you can download E tax.
The greatest benefit of using E-tax is that you can immediately see how much tax is refundable or how much you need to make up for it, but only if you have basic tax knowledge, so as not to be unable to get back the amount you deserve because you don't know how much Claim you can get. Or Claim too much to be censored by the ATO.
Use E-tax to file your own tax returns, and the information you need to prepare includes:
- PAYG Payment Summary provided by the Employer (annual salary summary);
- Tax number;
- Bank account number (if you choose the way directdebit is chosen);
- Medicare card number (if any);
- Annual bank interest;
- Dividends on investments (if any) in shares;
- Rental income and expenses for investment housing (if any).
If this is the first tax return, no Notice of assessment,ATO will ask you to provide information that only you know, such as the full-year pre-tax salary on PAYG summary. If you have a spouse (husband / wife / cohabitation), you may need to fill in each other's information.
Finally, to fill in the bank account, ATO will automatically pay to this account, to determine the BSB and Account Number pairs.
After completing this, you enter the income and work expenses section, which is filled in depending on your personal circumstances.
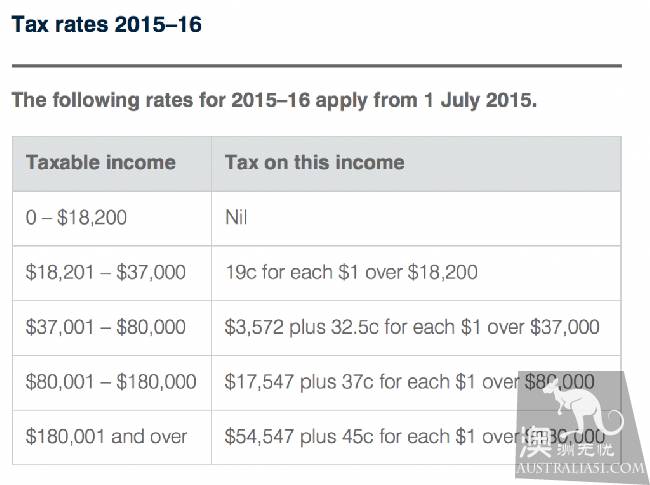
Current individual income tax rate in Australia (adjusted annually)

It is not difficult to find out from the above table that nearly half of the money of the high-income people has to be paid to the Inland Revenue Department, so we should study it well, make good investments, finance management, and tax rebates.
On tax rebate in Australia
There are many ways to reduce taxes reasonably, and it is often heard that most of Australia's truly rich and large companies pay little tax. So here are some tax rebate tips, let us reasonably avoid taxes.
If you have a business, a house, a car, a family, a variety of sources of income and expenses, generally do not report your own taxes, you should find a good accountant.
He can not only help you with the accounts, but also on behalf of your interests to respond professionally to the Inland Revenue Department's inquiries.

2, keep the evidence of reasonable expenditure.
A lot of reasonable expenses can be used in tax rebate. Because they are likely to be able to reasonably declare tax rebates. Such as computer upgrade, maintenance, battery, car repair, insurance, gasoline, hospitality, business expenses, etc.;
If there are investment housing, purchase furniture, house wear and tear, Internet access, cleaning, telephone charges and other invoices can also be provided.

3. If the spouse's income is a low or a non-income, one of the high-income sides can purchase a spouse's pension for the low-income side, with the highest possible tax benefit of $540.
Of course, there are other ways, for example, to change the average property owned by both parties to a higher proportion of the income side, or to pay household wages to the lower side (with written vouchers).
4, investment in Australian real estate, is a more popular tax rebate method in recent years. Especially in previous years, you can deduct taxes in depreciation, mortgage interest, maintenance, and so on.
5, if you have a few properties, try to live in the most value-added property. If you need to sell, it is best after at least a year, so you can enjoy a 50% value-added discount.
If you later want to sell your investment house, try to pay less VAT if your annual income becomes smaller, such as retirement, resignation, and illness.
If you have an investment home and want to get a pension, remember to transfer your assets five years before you retire, otherwise you will still be included in your retirement assets.
6, register a small business, this method can also help you tax rebate. In general, ordinary workers do not have many items to refund, but if involved in the operation, there will be plenty of tax rebate space.
For example, part-time stock, trading more than 40 times a year, can make the best money, but if you lose, you can report losses, as a negative number consolidated in your annual income, so that you can pay less tax.
In Australia, there are other tax avoidance methods. If you are a business operator, you can set up a family fund to spread the profits from the business to each family member.
About Australia's withholding tax
Australia is one of the few countries that practice withholding (negative gearing), and Australia's withholding policy is very different from that of other countries.

But what exactly is a withholding tax? Many friends may have heard of it as "a powerful tool to accumulate wealth quickly", but don't seem to know more about negative tax deductions.
In order to make everyone more happy and rich in Australia, today we will fully analyze the negative tax deduction!
What is negative tax deduction?
Don't be naive to think that "negative tax" comes with the word "tax" and that it is a tax category. In fact, it is a method of calculation that mainly exists in real estate investment. In a financial year, If the cash and non-cash expenditure on maintaining an investment property exceeds the investment income, (for example, if we need to pay interest on bank loans, water charges, electricity, municipal expenses, etc., plus depreciation of houses, etc., to maintain our business, Negative taxable income that exceeds our rent), we call it withholding tax.
Although tax deduction is not a tax category, but it is also linked to tax oh!
This is because negative taxable income can offset positive taxable income from other sources, such as wage earnings (Salary/Wage), capital gains (CapitalGain), and so on, thereby reducing taxable income and ultimately reducing tax payments.
The negative tax deduction policy allows owners to declare all property-related deductions, including mortgage interest-so they just need to make sure that the cost of investing in the property is greater than the rental income.
How to deduct tax?
Before we say how "deductible tax" is "withheld", there are two prerequisites to emphasize again:
- Beneficiaries invest in loans from banks (including real estate and stocks, etc.);
- Investment returns are lower than loan rates and other related expenses.
So, let's simulate what the whole process looks like:
Suppose you borrow five hundred thousand from the bank (an individual has paid a 20% down payment) and buy an investment home.
The annual interest rate for borrowing $500000 is 5%, and the annual interest rate is $25000;
The rent of the property is $500 per week and the annual income is $26000;
Depreciation fee of $15,000 for investment property;
Property management fee of $4,000 / year;
All of the above costs:
Income: $26000 for rental
Expenditure: interest $25000 depreciation $15000 property costs $4,000 / 44,000
Income against expenditure, loss of $18000
Let's say you earn $60,000 a year, and as a result of an investment loss, you'll be deducting $18,000 from the loss portion in calculating your personal tax payables.
As a result, the amount of tax you need to pay is reduced from $600,000 to $42000.
According to Australia's personal income tax rate, $37001 / 87000 is 32.5%.
Your payable amount is reduced from $60000 to $42,000, and you can pay $5850 less.
If your company has paid all taxes to the IRS at $60000, the IRS will give you a tax rebate of $5850 based on your "loss".
So, in Australia, if an individual suffers a loss as a result of borrowing and investment, the goverment will give "compensation" in accordance with the "negative tax deduction" policy.
From the above simple algorithm it is not difficult to see that most of the beneficiaries are able to borrow to buy investment housing. In particular, high-income people can get more and greater benefits from negative tax deductions!
You know. According to statistics, investors earning more than $180000 earn an average tax rebate of up to $23800! It's more than double the average rebate value of $10950!
So who does Australia benefit from?
According to statistics from the Australian Bureau of Statistics, many Australians have benefited. Of course, a sizeable proportion of those benefiting from negative deductions is the "ordinary working Australians" (average working Australians).

According to statistics for the previous two financial years, the wage groups benefiting from negative tax deductions include:
- Teachers and early Childhood educators: 61500
- Emergency Service personnel: 12315
- Nurses and elderly caretakers: 41980
- Cleaner: 6940
- Junior Office Clerk: 83280
- Hotel Service: 21555
- Barber: 1645
- Salesperson: 46450
- Transport workers (buses, trains, vans, couriers): 15525
- Craftsmen (carpentry, plumber, electrician, etc.): 34395
A total of 325585 of these ordinary working-class workers have raised and benefited from tax deductions, with 80% earning less than $87,000 a year. Ninety-one percent of them own only one or two investment properties.
But one thing worth noting is that 15,264 owners own at least 6 homes, declare investment losses, and 14,555 own 5!
As nearly 30, 000 Australians own five or more homes that can benefit from tax deductions, goverment loses as much as $5 billion a year in taxes.

