On february 18th the surging news jornalist found that the world`s first new report on the pathology of patients with pneumonia was published online on february 17th by the international journal of lancet respiratory medicine (The Lancet Respiratory Medicine). The team`s pathological analysis was not obtained through a complete autopsy, but through a patient`s post-death minimally invasive pathological examination (post-mortem biopsy), the same method as a clinically used tissue biopsy, only after the patient`s death.
The essay research team is from the infectious diseases diagnosis and treatment and research center of the fifth medical center of liberation army general hospital. One of the authors is professor wang fusheng, academician of the chinese academy of sciences and director of the national infectious diseases diagnosis and research center of the fifth medical center of liberation army general hospital.

The current clinical review shows that many of the patients with new coronary pneumonia are mild and moderate, but the disease may also die. Wang fusheng et al. mentioned in essay that the current fatality rate of the disease is 2%. Severe patients will be treated for massive alveolar damage and progressive respiratory failure, citing data as of february 15th: about 66580 cases were diagnosed and death 1524 were diagnosed.
However, there has been no pathological report of new coronary pneumonia since almost no previous autopsy or biopsy of living tissue was performed. In the study, the team studied the pathological features of a patient who died of a new coronary pneumonia by taking tissue samples after the patient died.
The team affirmed that "this study is in accordance with the provisions of the National Health and Health Commission and the Helsinki Declaration. our findings will help to understand the pathogenesis of new coronary pneumonia and improve clinical strategies for the disease. "
It is worth mentioning that the autopsy of the body of the new coronary pneumonia patient was completed on February 16 in the first case and the second case of the death of the new coronary pneumonia after the approval of the patient`s family members by law policy. Liu liang, a well-known expert in pathology of legal medical expert and president of the association of forensic experts in hubei province, attended the anatomy work. Conclusions are expected within 10 days.
In an interview with the journal of science and technology, chinese academy of engineering academician congbin, vice president of central, said:`we don`t have a clear pathological mechanism for the pathogenesis and death of xinguan virus infection, and we need to know about the clinical diagnosis of immune inflammation, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards), cellular hypoxia or oxygen disturbance, systemic inflammatory response syndrome (sirs) and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (mods).
Subject to autopsy:50-year-old male, with a history of travel in Wuhan, onset of 14 days
The patient,50, was admitted on january 21,2020 with symptoms such as fever, chills, coughing, fatigue and shortness of breath, according to essay. The patient reported having a history of travel in Wuhan from January 8 to 10, and on January 14, the first day of the disease, with initial symptoms of mild shivering and dry cough, but did not immediately seek medical attention until January 21.
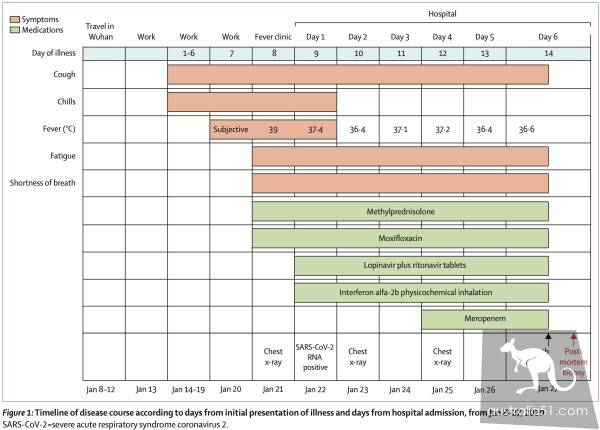
After the visit, the patient`s BREAST X-ray showed multiple plaque-like shadows in both lungs. The hospital took the patient`s throat swab. On January 22(the 9th day of onset), the patient was diagnosed with new coronary pneumonia according to the results of the China CDC (CDC) RT-PCR.
Subsequently, the patient was immediately admitted to the isolation ward to replenish oxygen through a mask. treatment options include interferon alfa-2b (5 million units, twice daily, atomized inhalation), lopinavir and ritonavir (500 mg, twice daily, orally) as antiviral treatment, moxifloxacin (0.4 g, once daily, intravenous) to prevent secondary sexy staining.
considering that the patient had severe shortness of breath and hypoxemia, the hospital also used methylprednisolone (80 mg per day, intravenously) to relieve inflammation in the lungs.
After taking the medicine, the body temperature decreased from 39.0°C to 36.4°C. However, his cough, dyspnea and fatigue did not improve.
onset day 12, patient breast x-rays showed both lung progressive infiltration and diffuse mesh shadowing. Because of claustrophobia, patients refused intensive care unit ventilator support several times.
On the 13 th day, the symptoms remained unchanged, but oxygen saturation remained above 95%.
Onset of the 14th afternoon, patients with hypoxemia and hyperventilation. despite receiving high flow nasal catheter oxygen therapy (100% concentration, flow rate 40 l/min), oxygen saturation decreased to 60% and cardiac arrest.
Doctors immediately administered invasive ventilation, chest compressions and epinephrine injections to the patient. Unfortunately, the rescue was unsuccessful, at 18:31 Beijing time on January 27.
The pathological features are very similar to those of SARS and MERS
The team took samples from the patient`s lung, liver, and heart tissues, and histological examination revealed bilateral diffuse alveolar injury, accompanied by cell fiber mucoid exudates. The right lung showed obvious pulmonary cell detachment and pulmonary hyaline membrane formation, indicating acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
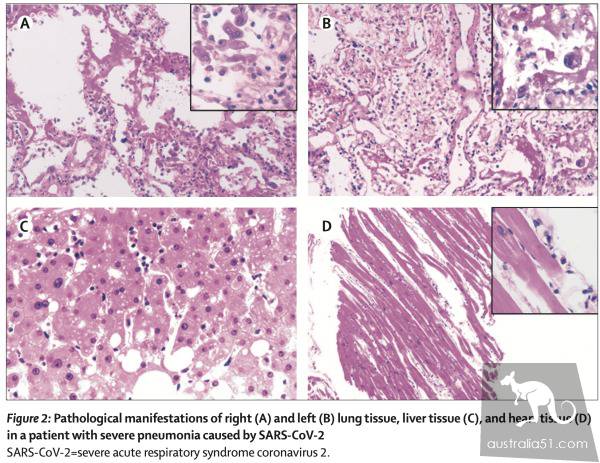
Pathological findings of right lung (A) and left lung (B) tissues, liver tissue (C) and heart tissue (D) in patients with severe pneumonia caused by a new type of coronary virus (SARS-CoV-2)
Interstitial mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltration was seen in both lungs, mainly lymphocytes. Multinucleated cells were identified in the alveolar cavity of the patient. Because of the enlargement of the pulmonary cells caused by the enlargement of the nucleus, there were amphiphilic granular cytoplasm and prominent nucleolus in the cells, which showed diseased toxicity cell lesions. No obvious virus inclusions were found in the nucleus or cytoplasm.
The team mentioned that the pathological features of new coronary pneumonia are very similar to those of patients with SARS and Middle Eastern respiratory syndrome (MERS).
in addition, liver samples from patients with neocrown pneumonia showed moderate microvascular steatosis, as well as mild hepatic lobule and portal vein activity, suggesting that the injury may be caused by neocrown virus infection or drug-induced liver injury.
There is a small amount of mononuclear inflammatory infiltration in the space of the heart tissue, but there is no other substantial damage in the heart tissue.
the study team performed flow cytometry analysis of the patient`s peripheral blood. The results showed that the number of CD4 and CD8 T cells in the blood was significantly reduced, but they were overactivated.
In addition, the concentration of highly proinflammatory CCR4CCR6Th17 in CD4T cells increased. At the same time, the team found that CD8 T cells had a high concentration of cellular toxicity granules, of which 31.6% were perforin-positive,64.2% were granulolysin-positive, and 30.5% were granulolysin- and perforin-positive.
The findings suggest that the overactivation of T cells, manifested by the increase in Th17 and the high cell toxicity of CD8 T cells, can partly explain why the patient developed severe immune damage.
X-ray images showed the patient`s pneumonia progressing rapidly, with differences in damage to the left and right lungs.
in addition, liver tissue presents with moderate microvascular steatosis and mild lobular activity, but there is no conclusive evidence to support this as a new coronavirus infection or drug-induced liver injury. no significant histological changes were found in the patient`s heart tissue, suggesting that neocrown virus infection may not directly damage the heart.
or consider timely and appropriate use of glucocorticoids and ventilators
the research team mentioned that although we do not recommend routine use of glucocorticoids for the treatment of new coronary pneumonia, according to the pulmonary edema and pulmonary hyaline membrane formation found in our pathological study, for severe patients, timely and appropriate use of glucocorticoid and ventilator treatment should be considered to avoid the deterioration of ards (acute respiratory distress syndrome).
in addition, lymphocytopenia is a common feature in patients with neocrown pneumonia and may be a key factor associated with disease severity and death rate.
our clinical and pathological findings in this new severe case of coronary pneumonia cannot only help identify the cause of death, but also provide new insights into the pathogenesis of new coronavirus-associated pneumonia, which may help doctors develop treatment strategies in time for similar severe patients and reduce the rate of death.

